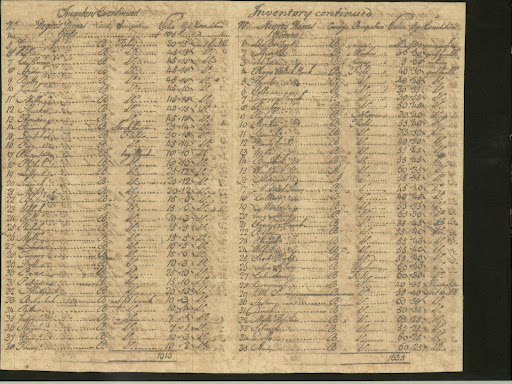
Inventory of enslaved people belonging to Castle plantation, Barbados, 1777.
In this article, Olivia Wyatt – Harewood’s volunteer researcher and an expert on the Lascelles family’s West Indian archive held at the Borthwick Institute – discusses the importance of surviving plantation inventories and how they can be used to recover the identities of enslaved African Caribbeans.
Deep within the Lascelles family’s West Indian archive lies the collection’s best preserved inventory of enslaved African Caribbeans – that of Castle plantation, Barbados, dated to 1777.
“It was created to enable plantation managers to calculate the value of their enslaved population and reinforce their subhuman status.”
This inventory (or list) records over 200 individuals by name as well as their ‘country’ of origin, occupation, computed age and condition. It was created to enable plantation managers to calculate the value of their enslaved population and reinforce their subhuman status. Ironically, however, historians can use this and other similar inventories, to ascertain lost names and reconstruct the lives of the marginalised, in turn helping us to return power to enslaved African Caribbeans. By using inventories to understand the ways in which experiences of disability, Blackness and naming practices operated on Lascelles-managed sugar plantations, we can diminish the attempts of slave masters who sought to eradicate the legacy of those they enslaved.
Some of the entries in the Castle Plantation inventory claim that the value of certain individuals was “nothing” because they had a “broken back” or were “very infirm”. At first glance, old age appears to be a key factor in this assessment, as the estimated age of ‘Great Joe’ and ‘Old Bridget’ was 80; Great Joe was only worth £10 despite being a “clarifier” and in “good health”.

However, a thirty-year-old man was also deemed valueless because he too was “infirm”. This implies that any injuries enslaved individuals acquired – most likely through work on the plantations – rendered them worthless, unable to emulate the labour of their counterparts. Even ‘Robin Almond’, at the age of just 10, is listed as valueless because he was also “infirm”. ‘Goany’, however, despite being only one month-old and “not fit for work”, was worth £5 because she was considered to have labour potential. These entries show that not only were enslaved African Caribbeans dehumanised by the brutal ways in which they were treated, but Black disabled people were considered worthless because they could not fulfill their assigned purpose, which reinforced the idea that Africans were only fit for servitude.

In an attempt to strip enslaved African Caribbeans of their identity, it became common practice to rename newly-arriving Africans as objects, or to give them European names. Two examples are ‘Black Silver’, a 45 year-old enslaved woman, and ‘Yellow Silver’, a Barbadian enslaved washer. The dehumanisation that naturally occurs when one’s heritage and name is replaced with that of a commodity reveals how slave owners intended to use naming practices to further oppress the enslaved population. These two names also represent the different shades of Blackness found on Caribbean plantations, which usually emerged as a result of the (typically coercive) sexual relations between enslaved women and their masters. ‘Black’ and ‘Yellow’ likely refer to the shades of the women’s skin, given that ‘Black Wallis’ and ‘Molatto William’ are other names on the plantation. ‘Yellow Silver’, like ‘Molatto William’, may have acquired her light complexion due to a mixed heritage. We do not know enough about the lives of the individuals listed in this inventory, though a growing amount of research has revealed that light-skinned African Caribbeans sometimes received preferential treatment due to their proximity to Whiteness. This could explain why ‘Molatto William’ was accorded one of the most valuable roles on the plantation.

Nonetheless, research has also revealed that enslaved African Caribbeans often had multiple names because they did not always adhere to the names that slave owners gave them. They also often played a role in the naming of their children and grandchildren. The names ‘Phibah’ and ‘Quashy’ appear frequently in the Castle plantation inventory, which have been identified as West-African “day names”, as ‘Phibah’ translates as Friday and ‘Quashy’ as Sunday. Historians agree that it was unlikely that slave owners selected these West-African names; therefore, these African naming practices are indicative of the ways in which the enslaved population retained their culture and humanity in the face of the brutality of slavery.
But what about Castle plantation itself and why this inventory was created?
The Lascelles family initially avoided owning plantations and instead operated as one of the biggest financiers of the Caribbean plantocracy and the sugar trade. Nonetheless, from 1773 they amassed many properties in Barbados, Jamaica, Grenada, and they sold their last plantation in 1975. Alongside managing their own plantations, the Lascelles provided loans for other planters and controlled some plantations as mortgagees in possession. The Castle plantation in the parish of St Lucy in Barbados was one such plantation. The Sober family owned it in name, but the management of the estate was overseen by representatives of the Lascelles family, and its produce was consigned to the Lascelles’ commission house in London until the mortgage was repaid. To determine the specifics of this mortgage, surveyors composed a full inventory of the Castle plantation’s enslaved population, cattle and horses in 1777. This document was originally drafted therefore to reaffirm the assigned status of enslaved African Caribbeans as property, but this blog has demonstrated how it can today be used to recover their humanity and ensure that they are never forgotten.
Olivia Wyatt
HHT Volunteer Researcher









